
The formula to calculate depreciation expense using sum-of-the-years‘ digits is shown below. In the second full year of the asset’s life, the amount of depreciation will be $40,000 (4/15 of $150,000). In the third full year of the asset’s life, the depreciation will be $30,000 (3/15 of $150,000). The fourth year depreciation will be $20,000 (2/15 of $150,000), and the fifth year will be $10,000 (1/15 of $150,000). Remember that the total amount of depreciation during this asset’s useful life should be $150,000. In later years, when the depreciation amount is smaller, the net income will be overstated.
Accounting Ratios
- Founded in 2017, Acgile has evolved into a trusted partner, offering end-to-end accounting and bookkeeping solutions to thriving businesses worldwide.
- The same company, with the exact same assets, would appear to be earning different amounts of profit and have assets carried at different values on the balance sheet, depending upon which depreciation method was utilized.
- In other words, the difference is in the timing of when the same total amount of depreciation will be reported.
- In addition, Mega Coffee is faced with a $400,000 installation charge to ensure that its computers are installed correctly and function at full capacity.
- Consider coffee company Mega Coffee, which is ready to expand into its new office headquarters.
Before calculating how much depreciation is charged to each accounting period in Step 5, we first need to calculate the depreciation expense for each year of the asset life. We need to count the remaining useful life from the asset’s timeline rather than the accounting periods’ perspective. The following example shows how you can work your way through each of the above steps to calculate depreciation using the sum of the years’ digits method. Like the sum of the years’ digits calculated in Step 1, the depreciation base does not change over the asset’s life and therefore only needs to be calculated once.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sum-of-the-Years’ Digits Method of Depreciation
On the other hand, the fixed asset that provides stable benefits from year to year during its useful life, e.g. building, is not suitable for the sum of years digits depreciation. Instead, the straight-line depreciation method is more suitable if that is the case. For calculating depreciation for the asset’s first year that ends on 30 September 2021 (Year 1), we will count the remaining useful life of 4 years. For the next year of the asset’s life that ends on 30 September 2022 (Year 2), the remaining useful life will be counted as 3 years.
Step 1 of 3
As companies continue to navigate dynamic economic environments, understanding and effectively applying the SYD method can enhance financial management and planning strategies. In addition, the calculator provides a sum of the years digits depreciation schedule setting out for each period, the beginning asset book value, the depreciation expense for the period, and the ending asset book value. The sum-of-years digits method of depreciating assets has the effect of increasing the value of net income because it discounts expenses over time.
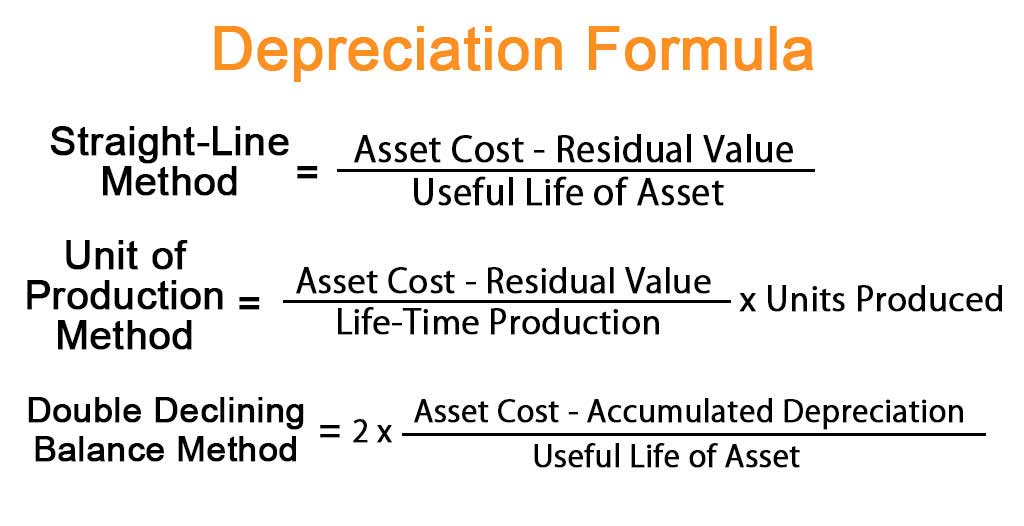
Depreciation determined in this way constitutes the annual depreciation expense, which is applied to the cost of acquisition or construction of the asset to be depreciated rather than the asset’s written-down value. The simplest and most common method of depreciation is the straight-line basis method of depreciation. The resulting number is then divided by the estimated useful life of the asset. Enter the period for which you want the sum of the years digits depreciation expense. The calculator will also produce a depreciation schedule setting out for each period, the beginning asset book value, the depreciation expense for the period, and the ending asset book value.
What is the Matching Principle in Accounting? [Explained]
This has the effect of making profits higher than they would be if they were calculated using the more traditional approach of straight-line Depreciation. This approach requires straight-line Depreciation rates and an asset’s useful life (which is the time period over which it will be used/depreciated). Finally, cost per equivalent unit calculator this method requires management to determine the appropriate Depreciation rate. According to the sum of years‘ digits method, the Depreciation expense is greater in earlier years (due to higher depreciable cost) and decreases over time until it becomes zero at the end of the asset’s useful life.
Accountingo.org aims to provide the best accounting and finance education for students, professionals, teachers, and business owners. Depreciation charges for the first two years of the asset are $45,000 and $30,000 respectively (refer the solution of the example above in case of confusion). Deskera is an all-in-one software that can overall help with your business to bring in more leads, manage customers and generate more revenue. Although the benefits of the sum of years method outnumber the disadvantages, it is important to take note of these.
In the example above, your straight-line depreciation expense would have been $20,000 each year—$100,000 x 1 /5. Additionally, in later years, your depreciation deduction for this asset will be lower under the sum of the years‘ digit method. The table below summarizes the breakdown of the depreciation expenses for each year.
When you depreciate an asset, you recognize an expense that represents the value of the asset used during the period. Finally the sum of years depreciation calculator works out the depreciation expense for the period entered in step 4. The first step is to calculate the sum of the years digits (SYD) for the useful life of the asset using the sum of years digits formula. Furthermore, management can choose straight-line depreciation for financial reporting purposes and a special form of accelerated depreciation for tax purposes. As with the double-declining-balance method, the sum-of-the-years‘ digits method allocates more depreciation in the early years and less in later years.
