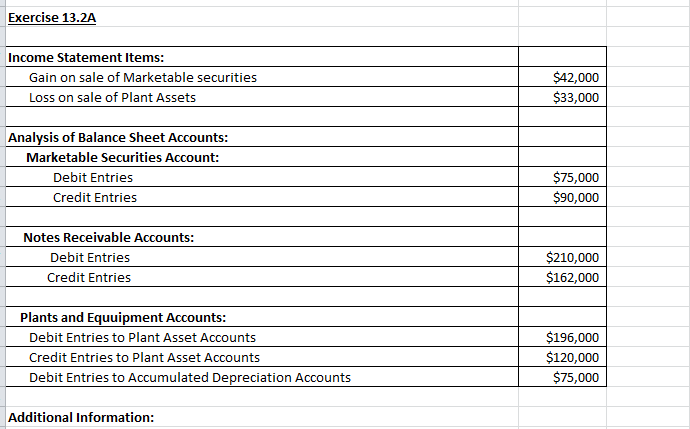
Long-term liabilities, on the other hand, are due at any point after one year. Journalize the transactions and work out the value at which the investments should appear on the balance sheet of the company as at 30 Mar. The manner in which a company reports the changes in the market price of these securities vary, but it affects several parts of the financial statements.
Are marketable securities current assets?
- This is because shareholders have partial ownership of the company that they have invested in.
- High liquidity refers to the ability to resell the asset with there being many buyers available to purchase, thus reducing the amount of time to convert the assets into cash.
- She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more.
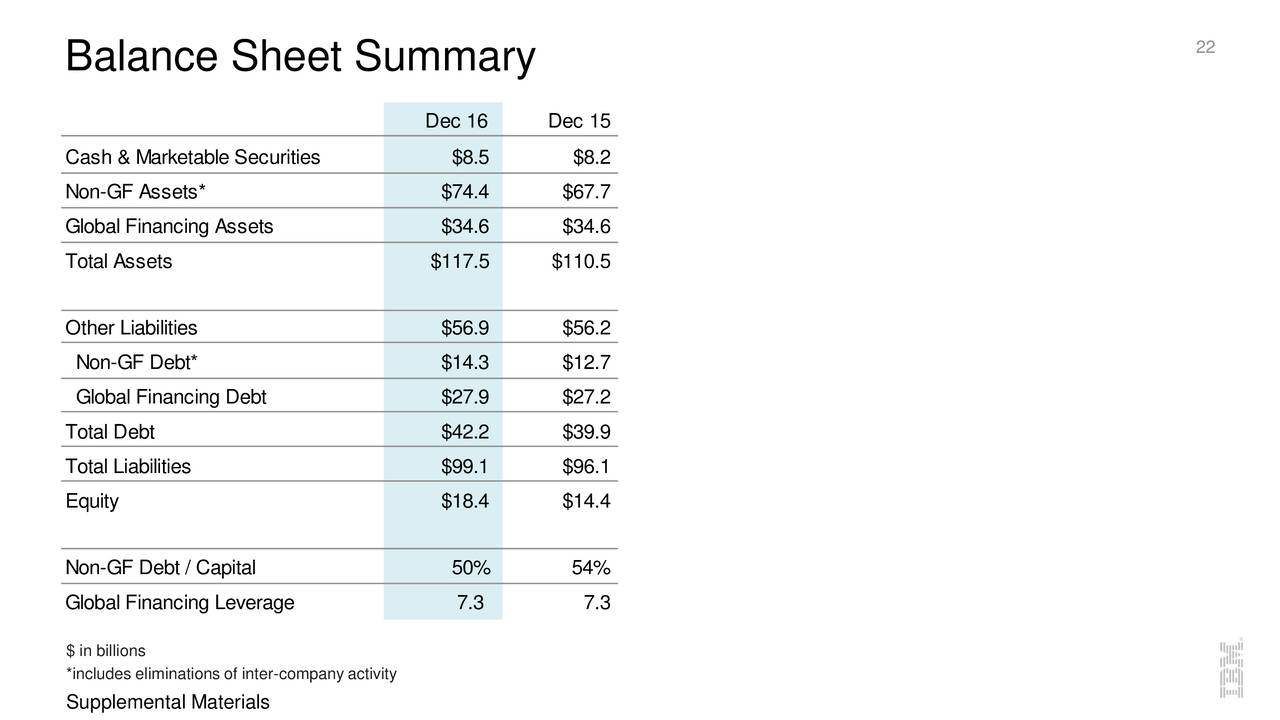
- The image below is an example of a comparative balance sheet of Apple, Inc.
- Investing in marketable securities is much preferred to holding cash in hand because investments provide returns and therefore generate profits.
- Additionally, marketable securities can be more advantageous than cash since they may generate a positive return, though this is not always the case.
Employees usually prefer knowing their jobs are secure and that the company they are working for is in good health. That’s because a company has to pay for all the things it owns (assets) by either borrowing money (taking on liabilities) or taking it from investors (issuing shareholder equity). Marketable securities differ from cash equivalents in the sense that cash equivalents typically have a maturity of 3 months or less while marketable securities may have a maturity of up to 12 months.
Accounting for Marketable Securities
Without an easily accessible market that investors and buy and sell securities on, a financial instrument is consider a non-marketable security. Marketable securities are defined as investments with short-term maturities that can be easily sold on public exchanges such as the Nasdaq and NYSE. While accounting for convertible bonds and debt with examples their ease of sale makes them attractive, it’s important to remember that marketability doesn’t guarantee profitability. As with any investment, understanding the characteristics, risks, and market dynamics of marketable securities is key to using them effectively in a financial strategy.
What Are Marketable Securities in Accounting?
These securities are essential investment classes and are favorites of major corporations. As noted in the below picture, Microsoft has more than 50% of its Total Assets as Short Term Investments or Marketable Securities. There are a few common components that investors are likely to come across. PwC refers to the US member firm or one of its subsidiaries or affiliates, and may sometimes refer to the PwC network. This content is for general information purposes only, and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with professional advisors. A secured credit card is a credit card where you provide a security deposit, and the card issuer bases your credit limit on that deposit.
Stocks As Securities
(Look at the equity section of the balance sheet of your favorite publicly traded company, and you will almost surely see Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income there. Assets that are held for trading purposes are recorded on the balance sheet at their fair value. Trading assets are bought and held primarily for the purpose of selling in the near term to generate profits on short-term price differences.
They are particularly appealing to anyone who thinks common stocks are too risky. They have the benefit of fixed dividends that are paid before common stockholders. Many types of marketable securities are readily accessible to individual investors including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and ETFs. This makes it easy for investors to buy any of the securities mentioned above, as there are usually minimal limitations outside of a simple brokerage account needed to get started. Companies and investors hold marketable securities instead of cash to potentially increase its net assets.
These securities are normally held by a company instead of cash and will have cashflows distributed or are interest-bearing. In most cases, companies strive to hold bonds as marketable securities. These types of investments are more ideal for those seeking short-term capital preservation. Another common form of marketable securities are stocks, as this type of marketable security is easily exchanged and have a slight opportunity for capital appreciation.
And if you have a secondary market, it provides a much more accurate price for investors. By investing in a variety of marketable securities, investors can achieve a diversified portfolio that spreads risk across multiple assets. This can help to reduce specific investment risks in addition to offering the potential for attractive returns. For corporate accounting, unmarketable securities are typically classified as long-term investments.
So if you remain unsure about how liquid a company is, remember that the line items occur in order of liquidity or the ability to convert to cash quickly. First, the marketable securities are at the top of the balance sheet and are under the balance sheet’s current assets section. Many companies will list if the marketable securities are a part of working capital calculations. For example, the description of adjusted working capital views only operating assets and liabilities. They exclude financing assets or liabilities, such as short-term debt and other marketable securities. These guaranteed dividends and safety from insolvency make preferred shares a tantalizing investment opportunity.
All investments involve risk, including the possible loss of capital. Before making decisions with legal, tax, or accounting effects, you should consult appropriate professionals. Information is from sources deemed reliable on the date of publication, but Robinhood does not guarantee its accuracy. Some issuers of marketable securities may create hybrid marketable securities that combine elements from equity and debt marketable securities. For example, a convertible bond is a debt security that includes a clause allowing you to convert the bond into a number of common shares under specific conditions. Another example of hybrid marketable securities is an equity warrant that grants you the right to buy a number of shares at a set price during a limited period.
