
Operating leverage is the extent to which a business can increase its operating income by increasing sales. Degree of operating leverage (DOL) is the multiple by which operating income changes in response to a change in sales. Operating leverage can also be measured in terms of change in operating income for a given change in sales (revenue). This means a 10% increase in sales would lead to a 26.7% increase in operating income.
Quick Ratio: (Definition, Formula, Example, and More)
Operating income is equal to sales minus variable costs and fixed costs. The DOL measures the how sensitive operating income (or EBIT) is to a change in sales revenue. Once obtained, the way to interpret it is by finding out how many times EBIT will be higher or lower as sales will increase or decrease respectively.
Operating Leverage Analysis Example
The degree of operating leverage shows the change in operating income to the change in the revenues or sales of a company. Let’s say that Stocky’s T-Shirts sells 700,000 t-shirts for an average price of $10 each. Their variable costs are $400,000, and their variable costs per unit are $0.57 (i.e., $400,000/700,000). As a business owner or manager, it is important to be aware of the company’s cost structure and how changes in revenue will impact earnings. Additionally, investors should also keep an eye on this ratio when considering an investment in a company.
- In this best-case scenario of a company with a high DOL, earning outsized profits on each incremental sale becomes plausible, but this type of outcome is never guaranteed.
- Most of a company’s costs are fixed costs that recur each month, such as rent, regardless of sales volume.
- A company with low operating leverage has a large proportion of variable costs—which means that it earns a smaller profit on each sale, but does not have to increase sales as much to cover its lower fixed costs.
- After calculating the leverage by applying the formula, if the result is equal to 1, then the operating leverage indicates that there are no fixed costs, and the total cost is variable in nature.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
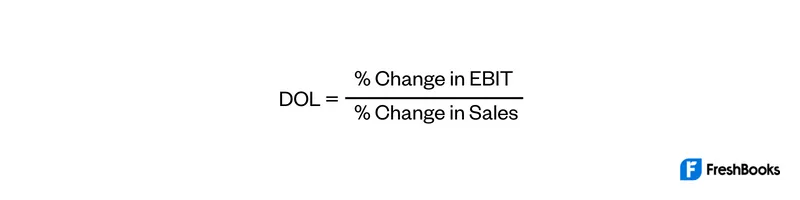
A DOL of less than 1 may indicate that a company needs to reassess pricing levels or streamline operations to reduce per-product production costs. Whatever your operating ratio is, it should always be used with other ratios, like profit margin or current ratio, to gauge the full health of your company. If a company expects an increase in sales, a high degree of operating leverage will lead to a corresponding operating income increase. But if a company is expecting a sales decrease, a high degree of operating leverage will lead to an operating income decrease.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Ratio analysis is the most commonly used method for assessing a firm’s financial health, profitability, and riskiness. Operating leverage is a measure of how revenue growth translates into growth in operating income. It is a measure of leverage, and of how risky, or volatile, a company’s best accounting software for advertising agencies operating income is. Operating leverage can be high or low, with benefits and drawbacks to each. When given the choice, most businesses would prefer to have a higher DOL, which gives them more flexibility, though it also means more risk of profits declining from a drop in sales.
Degree of Operating Leverage: Definition, Formula & Calculation
At the same time, a company’s prices, product mix and cost of inventory and raw materials are all subject to change. Without a good understanding of the company’s inner workings, it is difficult to get a truly accurate measure of the DOL. Higher fixed costs lead to higher degrees of operating leverage; a higher degree of operating leverage creates added sensitivity to changes in revenue.
This structure provides stability, as lower fixed costs mean the company doesn’t require high sales volumes to cover its expenses. If a company has high operating leverage, then it means that a large proportion of its overall cost structure is due to fixed costs. Such a company will enjoy huge changes in profits with a relatively smaller increase in sales. On the other hand, if a company has low operating leverage, then it means that variable costs contribute a large proportion of its overall cost structure. Such a company does not need to increase sales per se to cover its lower fixed costs, but it earns a smaller profit on each incremental sale. By contrast, a retailer such as Walmart demonstrates relatively low operating leverage.
The change is calculated at a given change in the revenues or sales. The companies most commonly calculate the degree of operating leverage to measure the operating risk. The combination of fixed and variable costs gives rise to operating risk. In fact, operating leverage occurs when a firm has fixed costs that need to be met regardless of the change in sales volume.
In most cases, you will have the percentage change of sales and EBIT directly. The company usually provides those values on the quarterly and yearly earnings calls. Basically, you can just put the indicated percentage in our degree of operating leverage calculator, even while the presenter is still talking, and voilà. Yes, industries that are reliant on expensive infrastructure or machinery tend to have high operating leverage. For example, airlines have high operating leverage because the cost of carrying an additional passenger on a plane is quite low. Much of the price of a restaurant meal is in the ingredients and labor, meaning they’ll have low operating leverage.
